This experiment works on the basis that liquids have different densities. Various immiscible (will not mix) liquids are placed in a graduated cylinder to see which ones are the most and least dense.
Methodology
Materials
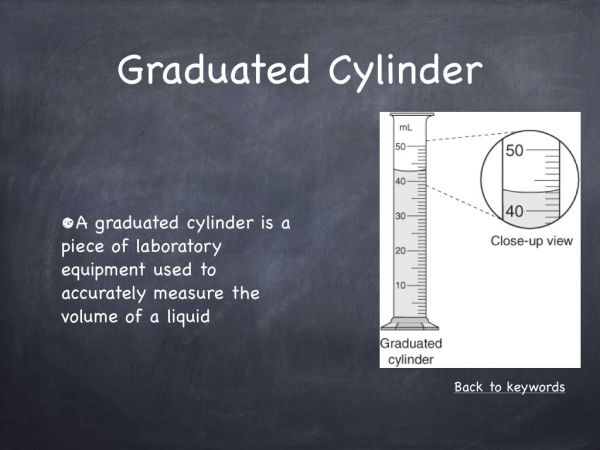
- 1000ml graduated cylinder
- Pipette
- Blue food colouring
- Fairy liquid
- Honey
- Maple syrup
- Water
- Cooking oil
- Methylated spirits
- Milk
Method
Preparation:
Before this experiment, plan exactly how much of each liquid you are going to place into the graduated cylinder. 100ml is a good amount.
Demonstration:
The honey creates the lowest level of the tower and can be squeezed into the graduated cylinder. The maple syrup can be directly poured on top of the honey. The fairy liquid can be poured directly onto the maple syrup. Note that all of the rest of the layers need to be pipetted into the graduated cylinder so that the liquids don’t mix. Add a layer of milk. The milk has to be full fat milk or else it will mix with the water layer. If the milk is fresh, it should float on the fairy liquid. If it’s old, its density increases and it will go below the fairy liquid layer. Add a layer of water. The water needs to be dyed with food colouring so that it stands out in the cylinder. Add a layer of oil. The final layer added is the methylated spirits. In the video, we used purple methylated spirits as it stood out. Red paraffin oil will also work.
Tips
Pipette every liquid above the fairy liquid into the cylinder to prevent any mixing.
*Precautions/Saftey
Theory behind the hook
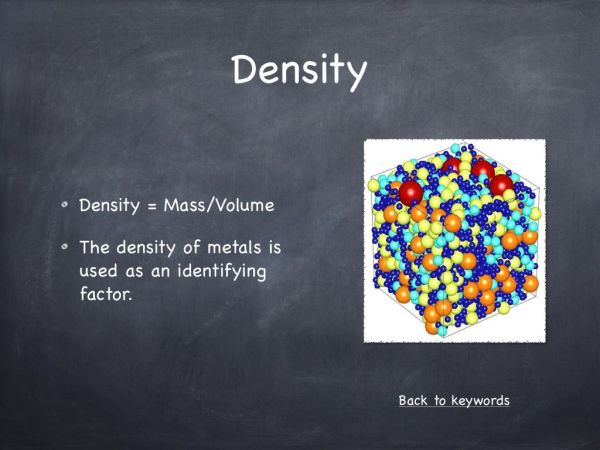
Often density is a concept that is associated with solids and not liquids or gases. Density is an abstract topic and this hook aims to make the concept more accessible to pupils especially as it uses everyday household liquids. This means that when certain liquids are mixed, they will separate. This is exemplified by the oil and water experiment at the start of the video (Figure 5). The density of water is 1gm/cm3, whereas the density of oil is lower at 0.9gm/cm3. Thus the oil floats on water. The experiment uses 7 different ingredients and is a very visual way to demonstrate a scientific principal.
How this hook works
This hook shows how liquids can be used to show some principles of density in a very colourful way. It is designed to appeal to visual learners. The tower builds slowly and allows time for the students to process what they are seeing before the teacher can question the pupils on the video.
Questions & Answers
- What is the densest liquid?
Honey is the densest because it is at the bottom of the flask. - What is the least dense substance?
The methylated spirits. - Why is the methylated spirits dyed purple?
This is so that people know it’s dangerous and that it is not to be ingested. - Why is the water dyed blue?
The water is dyed blue so that it is visible among the other layers. - What would happen if you put maple syrup on top of oil in a beaker?
The maple syrup would slowly make its way to the bottom of the beaker because it has a higher density.
Cross Curricular Links
Home Economics:
The experiment utilised a number of different ingredients that would be used in Home Ec. Class. Due to differences in density, these substances don’t mix. Therefore, they are not used for baking. The experiment also shows the use of food dye to drastically change the colour of a substance.
Art:
This experiment can be conducted in a number of ways. If slightly different substances are used, more colourful results can be obtained (e.g. paraffin oil for red or using different food dyes for water). For the tower to stand out, contrasting and bright colours need to be used. This links into the art curriculums study of colour, primary colours and mixing colours.
Real world links:
Oil has a lower density than water and this is why oil spillages at sea are so dangerous and detrimental to the environment. The British Petroleum oil spillage in the Mexican gulf is a prime example. It is often said that dilution is the solution to pollution, but because oil and water don’t mix, oil cannot be diluted. Different polymers can be used to absorb the oil and minimise the effects of the spillage.
Numeracy
The density of water is 1gm/cm3. Anything that floats on water has a density lower than 1. Anything that sinks has a density higher than 1.